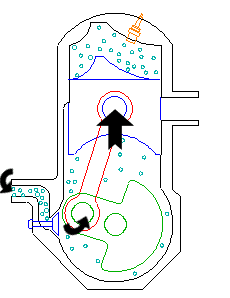
Intake
The fuel/air mixture is first drawn into the crankcase by
the vacuum that is created during the upward stroke of the
piston. The illustrated engine features a poppet intake valve;
however, many engines use a rotary value incorporated into the
crankshaft.
the vacuum that is created during the upward stroke of the
piston. The illustrated engine features a poppet intake valve;
however, many engines use a rotary value incorporated into the
crankshaft.
Crankcase compression
During the downward stroke, the poppet valve is forcedclosed by the increased crankcase pressure. The fuel mixture
is then compressed in the crankcase during the remainder of
the stroke.
Transfer/Exhaust
Toward the end of the stroke, the piston exposes the intakeport, allowing the compressed fuel/air mixture in the
crankcase to escape around the piston into the main cylinder.
This expels the exhaust gasses out the exhaust port, usually
located on the opposite side of the cylinder. Unfortunately,
some of the fresh fuel mixture is usually expelled as
well.
Compression
The piston then rises, driven by flywheel momentum, andcompresses the fuel mixture. (At the same time, another intake
stroke is happening beneath the piston).
Power
At the top of the stroke, the spark plug ignites the fuelmixture. The burning fuel expands, driving the piston
downward, to complete the cycle. (At the same time, another
crankcase compression stroke is happening beneath the piston.)
Since the two stroke engine fires on every revolution of the
crankshaft, a two stroke engine is usually more powerful than a
four stroke engine of equivalent size. This, coupled with their
lighter, simpler construction, makes the two stroke engine popular
in chainsaws, line trimmers, outboard motors, snowmobiles,
jet-skis, light motorcycles, and model airplanes.
Unfortunately, most two stroke engines are inefficient and are
terrible polluters due to the amount of unspent fuel that
escapes through the exhaust port.
crankshaft, a two stroke engine is usually more powerful than a
four stroke engine of equivalent size. This, coupled with their
lighter, simpler construction, makes the two stroke engine popular
in chainsaws, line trimmers, outboard motors, snowmobiles,
jet-skis, light motorcycles, and model airplanes.
Unfortunately, most two stroke engines are inefficient and are
terrible polluters due to the amount of unspent fuel that
escapes through the exhaust port.





No comments:
Post a Comment